Electricity
Electricity is the presence of motion of electric charges. Electricity is all around us powering houses, offices and technologies
like our cell phones, computers, lights, soldering irons, and air conditioners.
We can’t imagine this world without electricity. Electricity gives light to us,
gives comfort, keeps us connected and provide almost all entertainment devices.
History of electricity
For thousands of years, people were fascinated by
lightning and people tried to put this power to practical use. We never knew
lightning was electrical until the famous kite experiment by Sir Benjamin
Franklin. Franklin in 1752 performed the experiment in which he flew a kite
with metal key in the string. As lightning struck, he received an electrical
shock as the string was wet and he was lucky he survived. Then he proved that
lightning was electrical.
After that for many years, scientists were trying
to find a way to use the electrical power to light up their homes. In 1879
American inventor Thomas Edison was finally able to produce a light bulb.
To understand electricity, we need to first
understand what electric charges are; from where they come and how do they
move.
Electric charges
Electricity is the motion of electric charges.
But in order to move electric charges, we need electric charge carriers. They
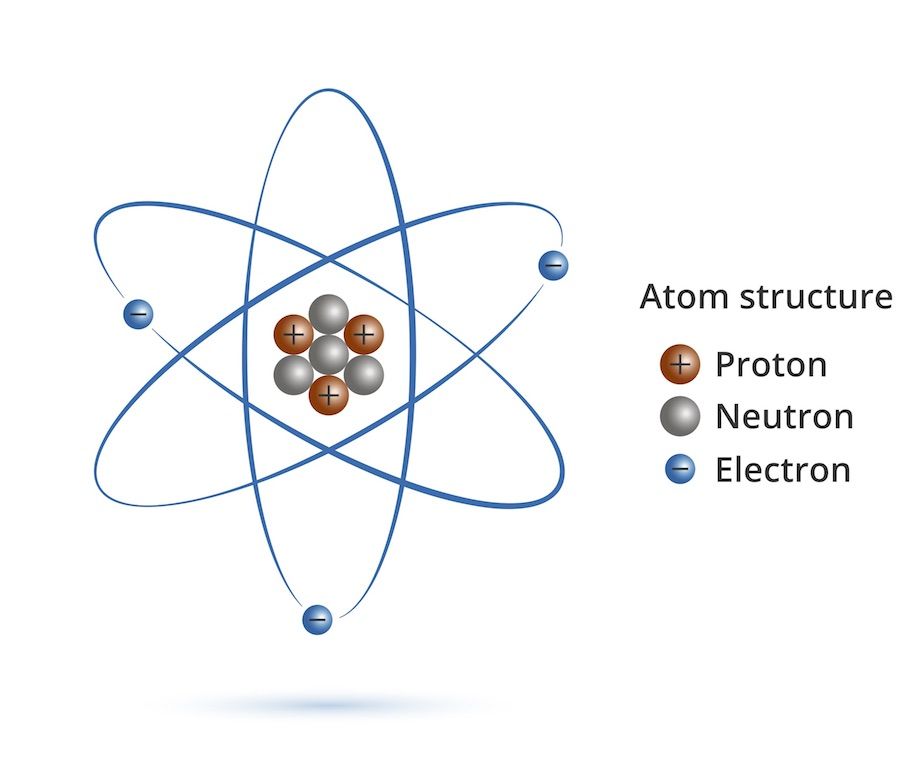
are electrons and protons. An atom mainly consists of three particles namely electron,
proton and neutron. Electron carries negative charge while proton carries
positive energy. Neutron is neutral and has no charge. Both electron and proton
carries same amount of charge but the type of charge varies.
But to make these charge carriers flow, there
works a force between them called electrostatic force.
Electrostatic force
Electrostatic force is the force that acts
between the electrons and protons. It states that charges of the same type repel
each other, while charges of opposite types are attracted together. Opposites
attract, and likes repel.
Amount of electrostatic force depends upon the distance between
them. If the electric charges are closer to each other, more will be the electrostatic
force between them.
Conductivity
Some substances have atoms that release an electron and they are
used as a conductor. A substance that allows electricity to pass through it is
called conductor. This type of elements aids the electron flow. These types of
elements are used to prepare wires. Examples of conductor are copper, silver,
gold, etc.
While insulators are elements which do not aid electron flow and
thus not let the electricity flow. They are used to make outer covering of wire
and other many safety materials. Examples of insulators are plastic, glass,
wood etc.
Electric
field
An electric field is the force
that fills the space around every electric charge or group of charges. Electric
fields are caused by electrical forces. Electrical forces are similar to gravitational forces in that
they act between things that are not in contact with each other.
Mathematically, the magnitude (or the strength) of an electric field at any
point is defined by the force experienced by the charge at that point divided
by the charge. This concept is written mathematically as E = F / q.
Electric field strength is measured in units of Newton/coulomb. Electric fields
are either static or dynamic.
Generation of electricity
There are various methods of generating
electricity. They are generated from different sources like heat, wind, sun,
nuclear elements and many others.
It is mostly generated by:
1. Thermal
plants: A thermal power station is a power station in which heat energy is
converted to electric power. In most of the places in the world the turbine is
steam-driven. Water is
heated, turns into steam and spins a steam turbine which drives an electrical
generator.
2. Nuclear
plants: Nuclear plants are one kind of thermal power plants but in them
heating source is the nuclear reactor.
3. Other
renewable sources: Electricity is also generated by natural elements like
sun, wind, water, etc. Some examples are solar panels, windmills, etc.
How bulb lights up?
When electricity is passed through the bulb, the
element called tungsten inside the bulb is heated to 2000K to 3000K, which is
less than the melting point of tungsten. Then, the energy is emitted in the
form of visible light in a continuous spectrum which we see, and the most
important part is most of the energy is given up as heating effect which falls
in infrared region. Also, the filament is placed under a low pressure inert gas
which slows down the oxidation of the filament tungsten, hence increasing its
lifeline.
Static electricity
What makes your hair standing while you bring a
plastic comb near them? This is not because of friction; this is because of
static electricity. Static force is created when electric charges which are
positive and negative are separated by an insulator and there is imbalance in
them. Means no. of positive charge carriers are not equal to negative charge
carriers.
Thus to create a balance between them, they can
even flow through best conductors like wood, plastic, glass, etc. and so we
experience static electricity.
Lightning is the best visible example of static
electricity. The ground consists of electrical charges and clouds also have
some electrical charges. They try to create a balance and the insulator here is
between the charges is air. And thus, static electricity is created and we see
the visible lightning bolt.
Thus, electricity is the natural phenomena from
which we can’t escape. Today we can’t imagine this world without electricity;
we are all dependent on our mobile phones, computers, internet connection and
many other things that work on electricity. Even if we escape from this gadgets
and lighting, it will still remain in nature from the lightning strike and
also the electrical signals in our brain.
Comments
Post a Comment