Ideal power source vs Practical power source
A source is a device which converts mechanical, chemical,
thermal or some other form of energy to electrical energy. The types of sources
available in the electrical network are voltage source and current source.
Voltage source is used to provide voltage to the load while current source is
used to apply current.
Voltage source
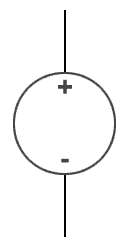
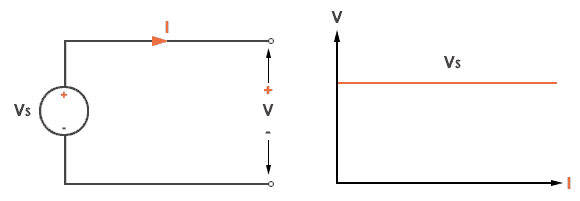
A voltage source is device which provides constant voltage
to load at any instance of time and is independent of the current drawn from
it. This type of source is known as ideal voltage source. Practically ideal
voltage source cannot be made. It has zero internal resistance. It is denoted
by this symbol.
The graph of voltage vs time represents the change in voltage of the voltage
source with respect to time. It is constant at any instance of time.
Voltage sources that have some amount of internal resistance
are known as practical voltage source. Due to this internal resistance, voltage
drop takes place. If the internal resistance is high, less voltage will be
provided to load and if the internal resistance is less, voltage source will be
closer to an ideal voltage source. Practical voltage source is thus denoted by
a resistance in series which represents internal resistance of source.
The graph represents the voltage of the voltage source with
respect to time. It is not constant but it keeps on decreasing as the time
passes.
Current source
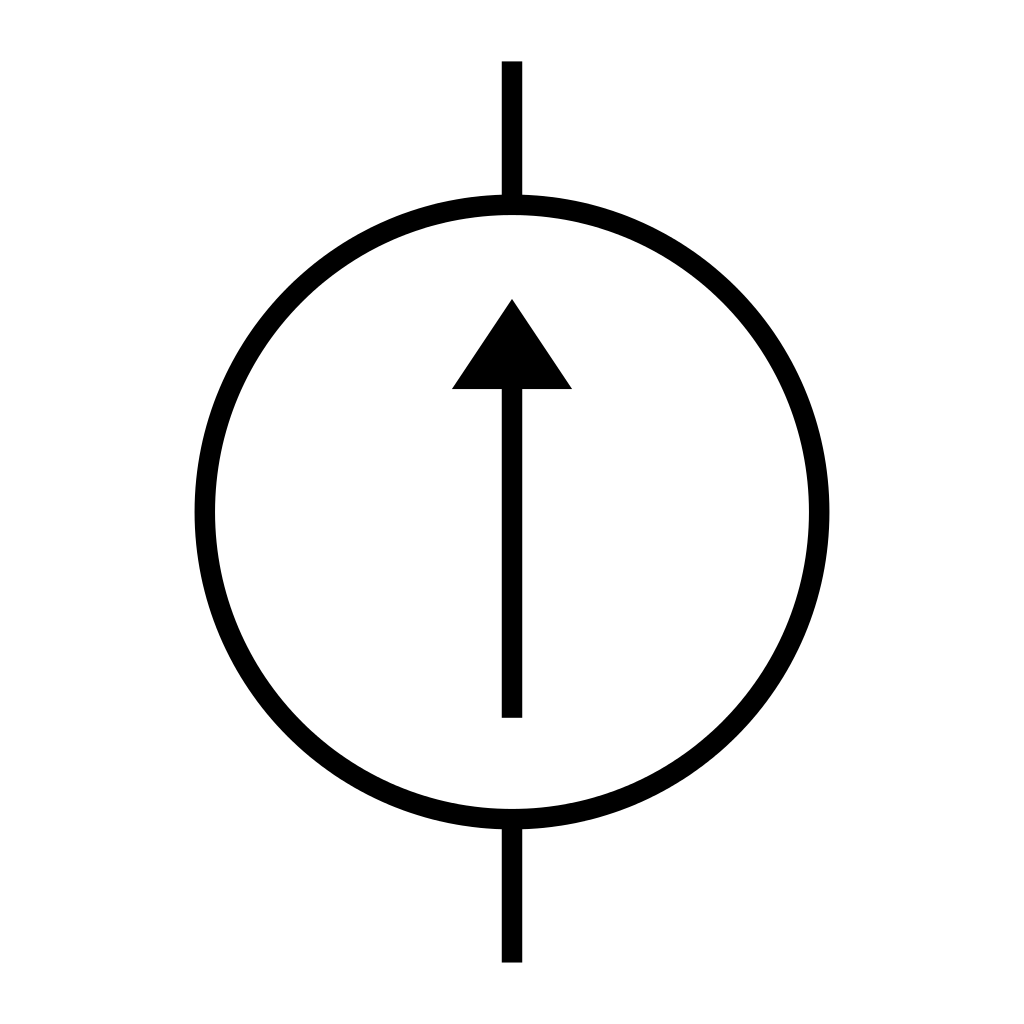
A current source is a device which provides constant current
to load at any time and is independent of the voltage supplied to circuit. This
type of current is known as ideal current source; practically ideal current
source is also not available. It has infinite resistance. It is denoted by this
symbol.
Why ideal current
source have infinite resistance?
A current source is used to power a load, so that load will
turn on. We try to supply 100% of the power to load. For that we connect some
resistance to transfer 100% of power to load because current always takes the
path of least resistance. So, in order for current to go to the path of least
resistance, we must connect resistance higher than load. This is why we have
ideal current source to have infinite internal resistance. This infinite
resistance will not affect voltage sources in the circuit.
Practical current
sources
Practically current sources do not have infinite resistance
across there but they have a finite internal resistance. So the current delivered
by practical current source is not constant and it is also dependent somewhat
on voltage across it.
A practical current source is represented as an ideal
current source connected with resistance in parallel.
The graph represents the current of the current source with
respect to time. It is not constant but it also keeps on decreasing as the time
passes.
Examples of current
and voltage sources
The examples of current source are solar cells, transistors
and examples of some voltage sources are batteries and alternators.
This was all about ideal and practical sources of power. The
ideal sources are very useful for calculations in theory but as ideal sources
are not practically possible, only practical sources are used in practical
circuits. The batteries we use are practical source of power and the voltage
and current decreases as we use it. Thus both are useful to us in their own
ways.


Comments
Post a Comment